概要
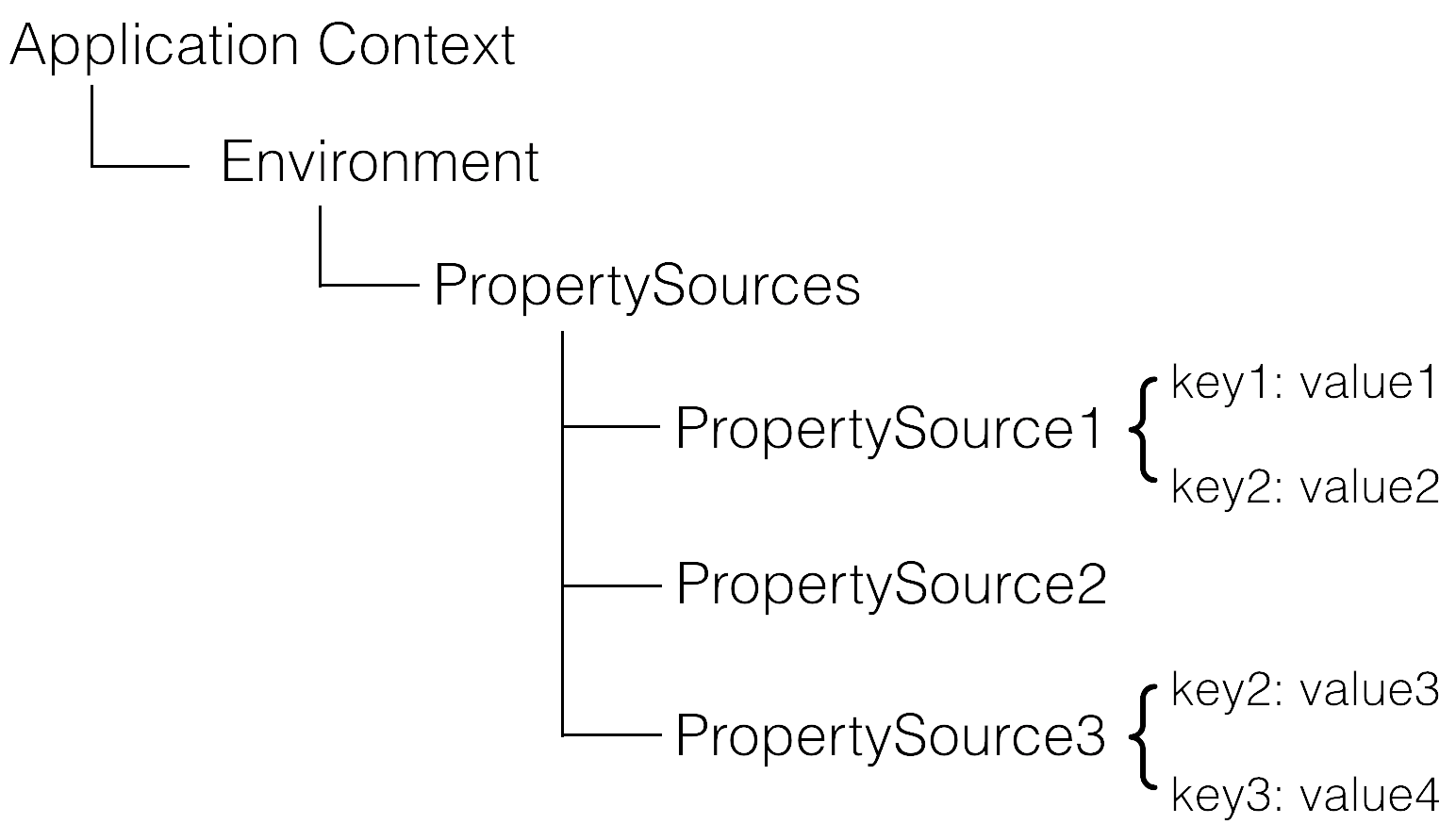
PropertySource:管理各种配置源的抽象类,即属性源PropertySources:用于统一管理和访问多个 PropertySource 实例PropertyResolver:通用属性解析
Environment:应用环境表示,提供属性访问,支持profile。ConfigurablePropertyResolver:属性解析配置,支持占位符解析。
Binder:配置绑定工具
大致关系图:
图片来自https://www.apolloconfig.com/#/zh/design/apollo-design?id=_31-和spring集成的原理
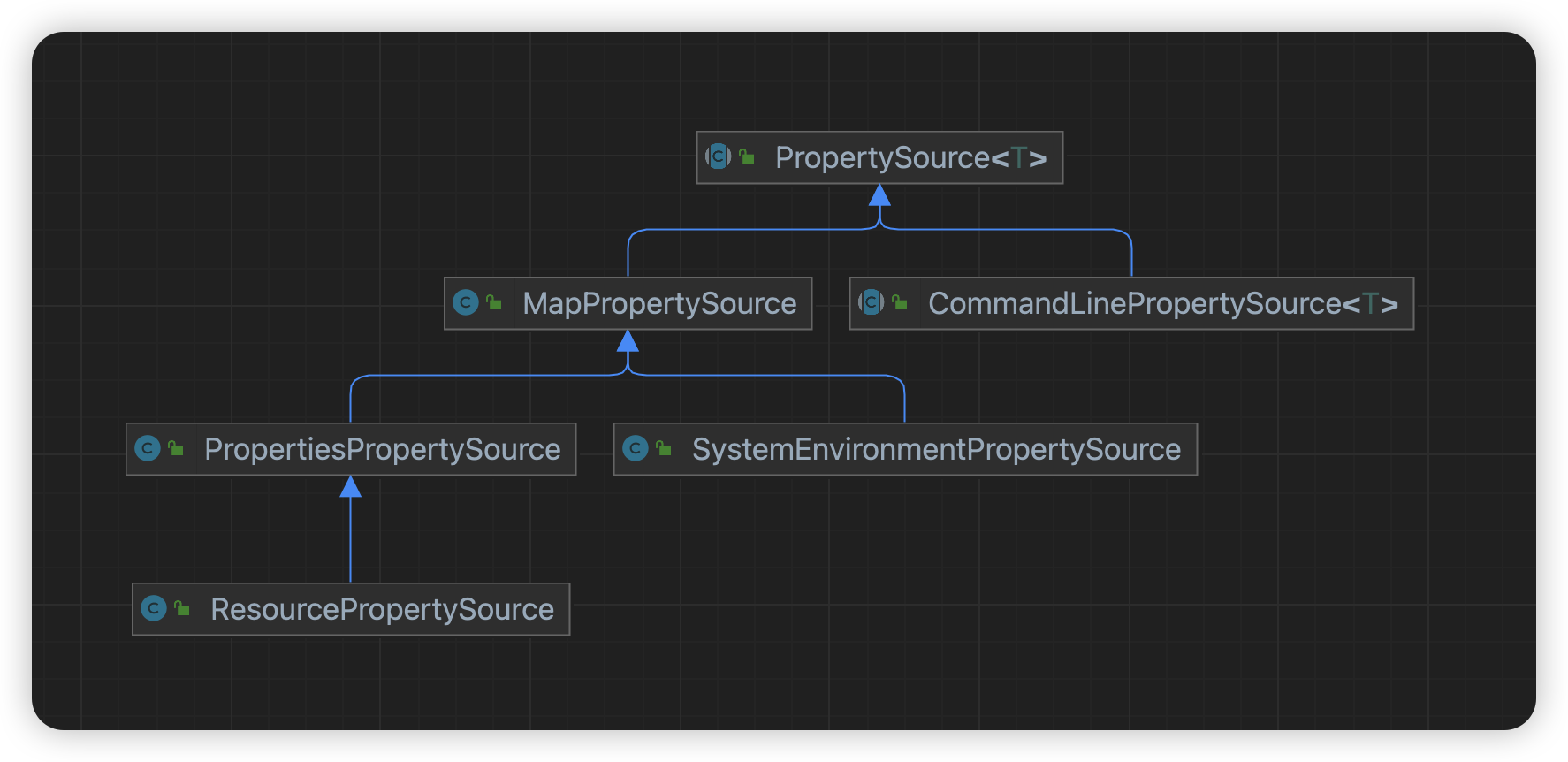
PropertySource
PropertySource是 Spring 框架中的一个关键抽象类,封装了一个属性源,属性源可以是一个Map、Resource对象、系统变量等等
PropertySources PropertySources 是一个Spring框架中的接口,用于表示和管理一组属性源(PropertySource),这些属性源包含了应用程序环境中的配置数据。该接口提供了一系列方法来检索、添加、替换和删除这些属性源,允许开发者以统一的方式访问不同来源的配置信息,如环境变量、系统属性、配置文件等。
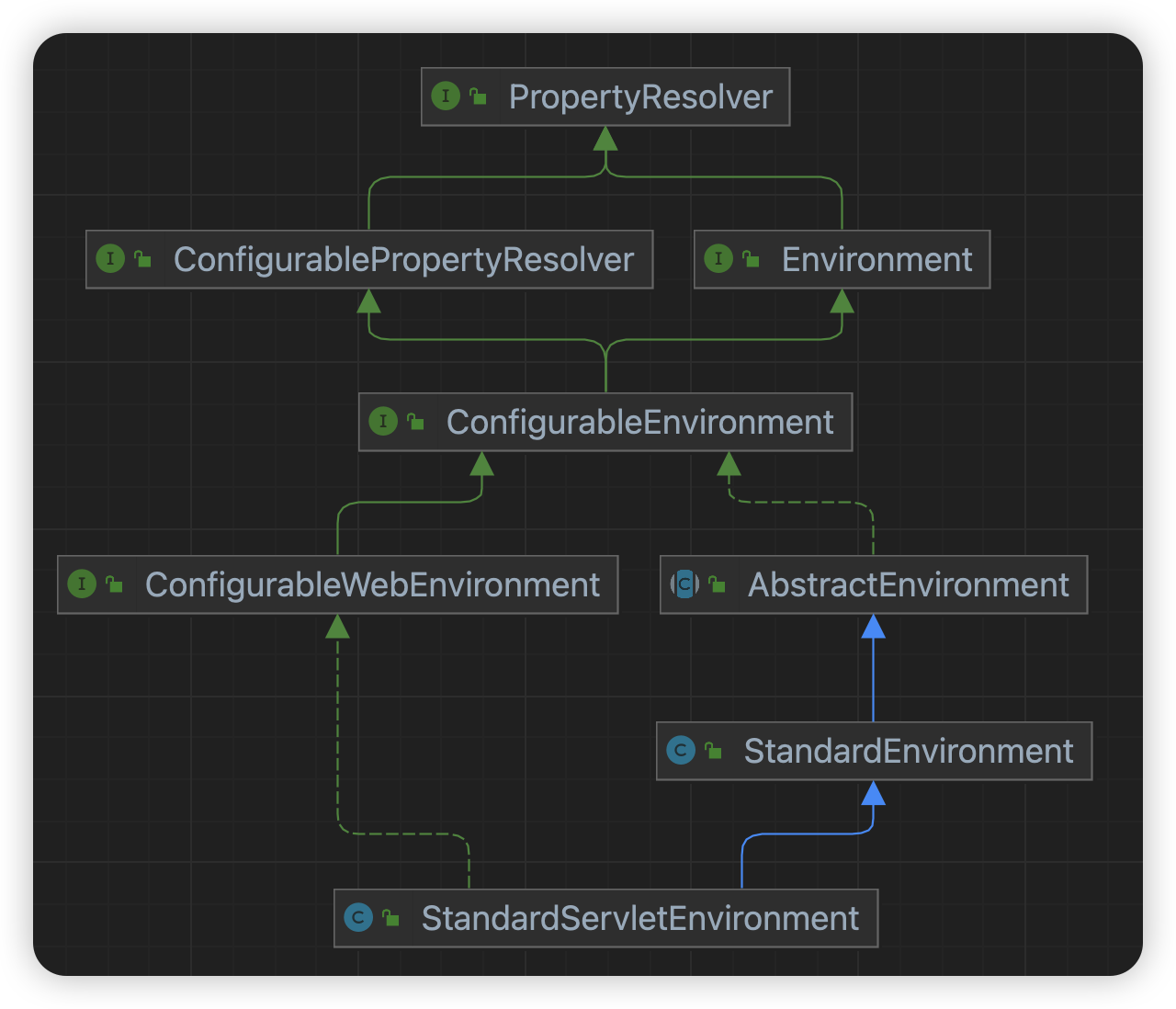
PropertyResolver PropertyResolver是一个顶层接口,提供了一套灵活且强大的机制来处理应用程序配置属性。它定义了一些获取属性值,以及解析占位符的方法,用于访问和操纵来自各种源的属性值。
Environment Environment 接口是 Spring 框架中的一个核心部分,它提供了一个统一的方式来访问各种外部化的配置数据(继承自PropertyResolver);支持配置文件(Profiles)的概念,可以在不同环境下进行条件性的配置,管理多个属性源。
可以看到Environment是继承了PropertyResolver接口的,只是增加了一些环境信息方法(profile)
其中Environment实例关于PropertyResolver接口的方法是通过组合模式实现的,内部持有一个PropertySourcesPropertyResolver实例。
ConfigurablePropertyResolver ConfigurablePropertyResolver 接口则增加了一些配置方法,在Spring中关键作用是提供灵活的配置属性解析。它支持占位符解析 ,并解析这些占位符为实际的配置值,提升配置的动态性和灵活性。
其他实现
ConfigurableEnvironment,增加了一些配置的方法,以及可以获取到内部的PropertySource列表。StandardEnvironment,非web上下文使用的环境实例。StandardServletEnvironment,web上下文使用的环境实例。
属性绑定 ConfigurationPropertySource 这是一个新的接口,不过它的实现类也是借助了PropertySource来实现,尽管他们之间没有任何继承关系。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public interface ConfigurationPropertySource { ConfigurationProperty getConfigurationProperty (ConfigurationPropertyName name) ; default ConfigurationPropertyState containsDescendantOf (ConfigurationPropertyName name) { return ConfigurationPropertyState.UNKNOWN; } default ConfigurationPropertySource withAliases (ConfigurationPropertyNameAliases aliases) { return new AliasedConfigurationPropertySource (this , aliases); } }
ConfigurationPropertySources提供了从environment中获取属性源构建ConfigurationPropertySource的方法:
1 Iterable<ConfigurationPropertySource> sources = ConfigurationPropertySources.get(environment);
Binder Spring提供了一个很强大的工具类Binder,依赖ConfigurationPropertySource
作用:可以将Environment或者ConfigurationPropertySource中的属性绑定到一个Java对象中
他有两个重要方法:bind()和bindOrCreate(),两个方法有多重重载方式,这里列举了两种
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class Binder { private final Iterable<ConfigurationPropertySource> sources; public <T> BindResult<T> bind (ConfigurationPropertyName name, Bindable<T> target, BindHandler handler) { T bound = bind(name, target, handler, false ); return BindResult.of(bound); } public <T> T bindOrCreate (ConfigurationPropertyName name, Bindable<T> target, BindHandler handler) { return bind(name, target, handler, true ); } }
Binder类还提供一个静态方法get()来构造Binder实例,可以从Environment实例获取PropertySources
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public static Binder get (Environment environment) { return get(environment, null ); } public static Binder get (Environment environment, BindHandler defaultBindHandler) { Iterable<ConfigurationPropertySource> sources = ConfigurationPropertySources.get(environment); PropertySourcesPlaceholdersResolver placeholdersResolver = new PropertySourcesPlaceholdersResolver (environment); return new Binder (sources, placeholdersResolver, null , null , defaultBindHandler); }
我们项目中常用于配置注入的@ConfigurationProperties,实现原理也是通过Binder
@ConfigurationProperties实现原理 @ConfigurationProperties注解在Spring Boot中常用来绑定属性到Java Bean中,不难猜出内部原理便是使用上面所介绍的Binder类来实现的。
使用该注解时常常搭配@EnableConfigurationProperties注解一起使用,@EnableConfigurationProperties的主要作用就是注册了一个ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessorBean
绑定的核心逻辑在ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (!hasBoundValueObject(beanName)) { bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean.get(this .applicationContext, bean, beanName)); } return bean; } private void bind (ConfigurationPropertiesBean bean) { ... try { this .binder.bind(bean); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new ConfigurationPropertiesBindException (bean, ex); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 BindResult<?> bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean propertiesBean) { Bindable<?> target = propertiesBean.asBindTarget(); ConfigurationProperties annotation = propertiesBean.getAnnotation(); BindHandler bindHandler = getBindHandler(target, annotation); return getBinder().bind(annotation.prefix(), target, bindHandler); } private Binder getBinder () { if (this .binder == null ) { this .binder = new Binder (getConfigurationPropertySources(), getPropertySourcesPlaceholdersResolver(), getConversionServices(), getPropertyEditorInitializer(), null , null ); } return this .binder; } private Iterable<ConfigurationPropertySource> getConfigurationPropertySources () { return ConfigurationPropertySources.from(this .propertySources); } private PropertySourcesPlaceholdersResolver getPropertySourcesPlaceholdersResolver () { return new PropertySourcesPlaceholdersResolver (this .propertySources); } private List<ConversionService> getConversionServices () { return new ConversionServiceDeducer (this .applicationContext).getConversionServices(); } private Consumer<PropertyEditorRegistry> getPropertyEditorInitializer () { if (this .applicationContext instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableContext) { return configurableContext.getBeanFactory()::copyRegisteredEditorsTo; } return null ; }
关键点在于使用Binder将ConfigurationPropertySource中的属性源和实际的ConfigurationPropertiesBean对象绑定在了一起,实现配置的注入。注意ConfigurationPropertySource中的属性源是带有prefix的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class PrefixedConfigurationPropertySource implements ConfigurationPropertySource { private final ConfigurationPropertySource source; private final ConfigurationPropertyName prefix; PrefixedConfigurationPropertySource(ConfigurationPropertySource source, String prefix) { Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null" ); Assert.hasText(prefix, "Prefix must not be empty" ); this .source = source; this .prefix = ConfigurationPropertyName.of(prefix); } }
参考: