什么是SPI机制?
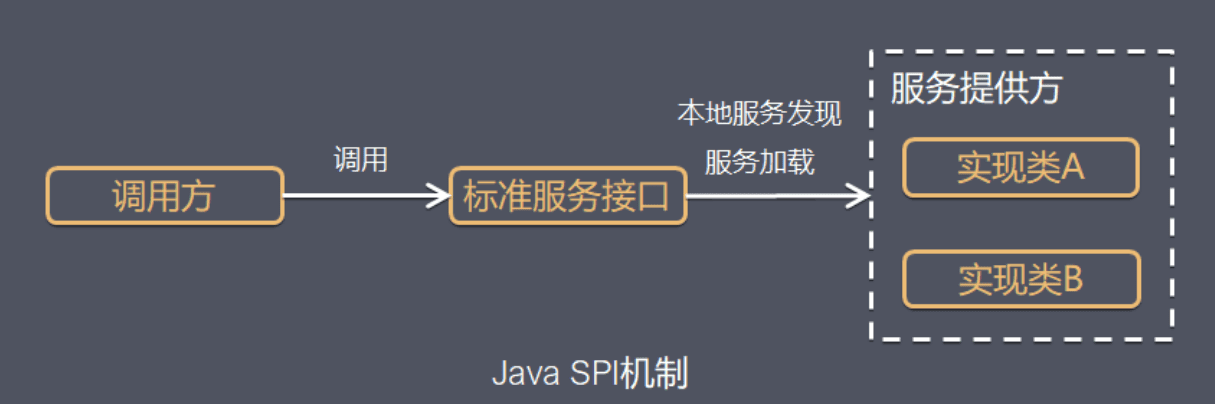
SPI(Service Provider Interface)
Java 中 SPI 机制主要思想是将装配的控制权移到程序之外,在模块化设计中这个机制尤其重要,其核心思想就是 解耦 。
本文探讨SPI在Java和SpringBoot中的实现以及具体的使用姿势
Java SPI Java SPI 中有四个重要的组件:
服务接口 :一个定义了服务提供者实现类契约方法的接口或者抽象类。服务实现 :实际提供服务的实现类。SPI 配置文件 :文件名必须存在于 META-INF/services 目录中。文件名应与服务提供商接口完全限定名完全相同。文件中的每一行都有一个实现服务类详细信息,即服务提供者类的完全限定名。ServiceLoader : Java SPI 关键类,用于加载服务提供者接口的服务。
简单看一个demo:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public interface Compresser { byte [] compress(byte [] bytes); byte [] decompress(byte [] bytes); } public class GzipCompresser implements Compresser { @Override public byte [] compress(byte [] bytes) { return "compress by Gzip" .getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); } @Override public byte [] decompress(byte [] bytes) { return "decompress by Gzip" .getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); } } public class ZipCompresser implements Compresser { @Override public byte [] compress(byte [] bytes) { return "compress by Zip" .getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); } @Override public byte [] decompress(byte [] bytes) { return "decompress by Zip" .getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); } }
编写SPI 配置文件:
在META-INF/services中创建cn.ppphuang.demoserver.serviceproviders.Compresser文件,注意文件名是标准服务接口类的全限定类名
1 2 cn.ppphuang.demoserver.serviceproviders.GzipCompresser cn.ppphuang.demoserver.serviceproviders.ZipCompresser cn.ppphuang.demoserver.serviceproviders.Compresser
接下来通过 ServiceLoader 加载服务:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public static void main (String[] args) { ServiceLoader<Compresser> serviceLoader = ServiceLoader.load(Compresser.class); for (Compresser service : serviceLoader) { System.out.println(service.getClass().getClassLoader()); byte [] compress = service.compress("Hello" .getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); System.out.println(new String (compress)); byte [] decompress = service.decompress("Hello" .getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); System.out.println(new String (decompress)); } } ------------- sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2 compress by Gzip decompress by Gzip sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2 compress by Zip decompress by Zip
常见SPI案例
JDBC SPI
SPI的使用非常广泛,一个比较出名的实现就是JDBC
在JDBC中,我们一般会通过DriverManager去创建与数据库的连接;而DriverManager会查找并加载classPath中不同的Driver的实现
Common-Logging(JCL)
Common-Logging apache是常用的日志库门面。只有接口(LogFactory),没有实现。具体方案由各提供商实现
Java SPI存在的问题 使用 Java SPI 能方便得解耦模块,使得接口的定义与具体业务实现分离。应用程序可以根据实际业务情况启用或替换具体组件。但是也有一些缺点:
不能按需加载 。虽然 ServiceLoader 做了延迟载入,但是基本只能通过遍历全部获取,也就是接口的实现类得全部载入并实例化。如果你并不想用某些实现类,或者某些类实例化很耗时,它也被载入并实例化了,这就造成了浪费。获取某个实现类的方式不够灵活 。只能通过 Iterator 形式获取,不能根据某个参数来获取对应的实现类。多个并发多线程使用 ServiceLoader 类的实例是不安全的。
Spring SPI Spring的SPI机制其实就是SpringBoot自动装配的原理。在SpringBoot的自动装配过程中,最终会加载META-INF/spring.factories文件,而加载的过程是由SpringFactoriesLoader加载的。
@SpringBootApplication → @EnableAutoConfinguration → @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
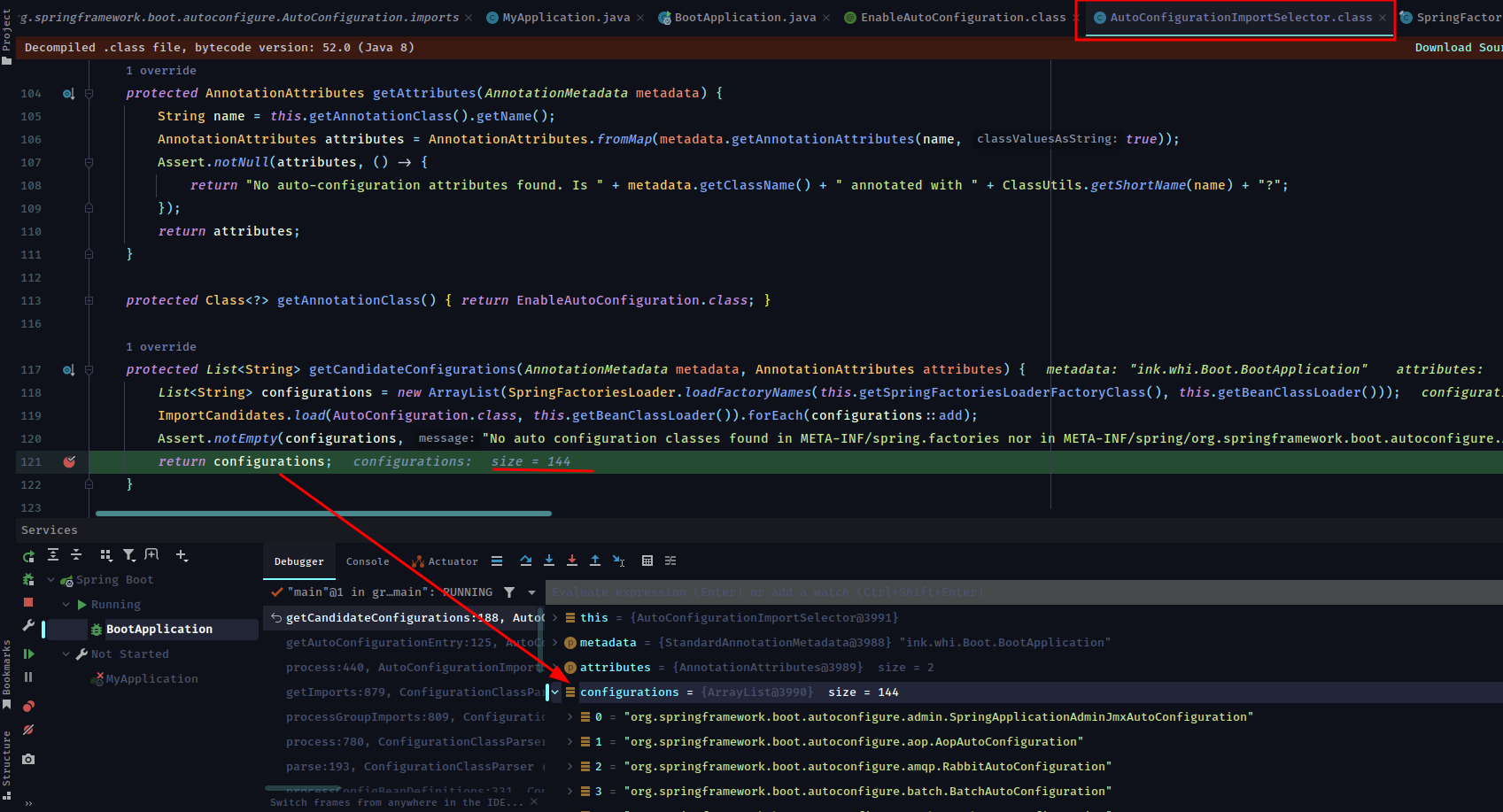
核心类AutoConfigurationImportSelector,这个类是自动装配的关键:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector , BeanClassLoaderAware, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered { @Override public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return NO_IMPORTS; } AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata); return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()); } protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry (AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return EMPTY_ENTRY; } AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata); List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations); Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes); checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions); configurations.removeAll(exclusions); configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations); fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions); return new AutoConfigurationEntry (configurations, exclusions); } } protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations (AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { List<String> configurations = ImportCandidates.load(AutoConfiguration.class, getBeanClassLoader()) .getCandidates(); ... return configurations; } private static final String LOCATION = "META-INF/spring/%s.imports" ;public static ImportCandidates load (Class<?> annotation, ClassLoader classLoader) { Assert.notNull(annotation, "'annotation' must not be null" ); ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = decideClassloader(classLoader); String location = String.format(LOCATION, annotation.getName()); Enumeration<URL> urls = findUrlsInClasspath(classLoaderToUse, location); List<String> importCandidates = new ArrayList <>(); while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = urls.nextElement(); importCandidates.addAll(readCandidateConfigurations(url)); } return new ImportCandidates (importCandidates); }
我们可以看一下最后获取到的需要注入的Bean信息:
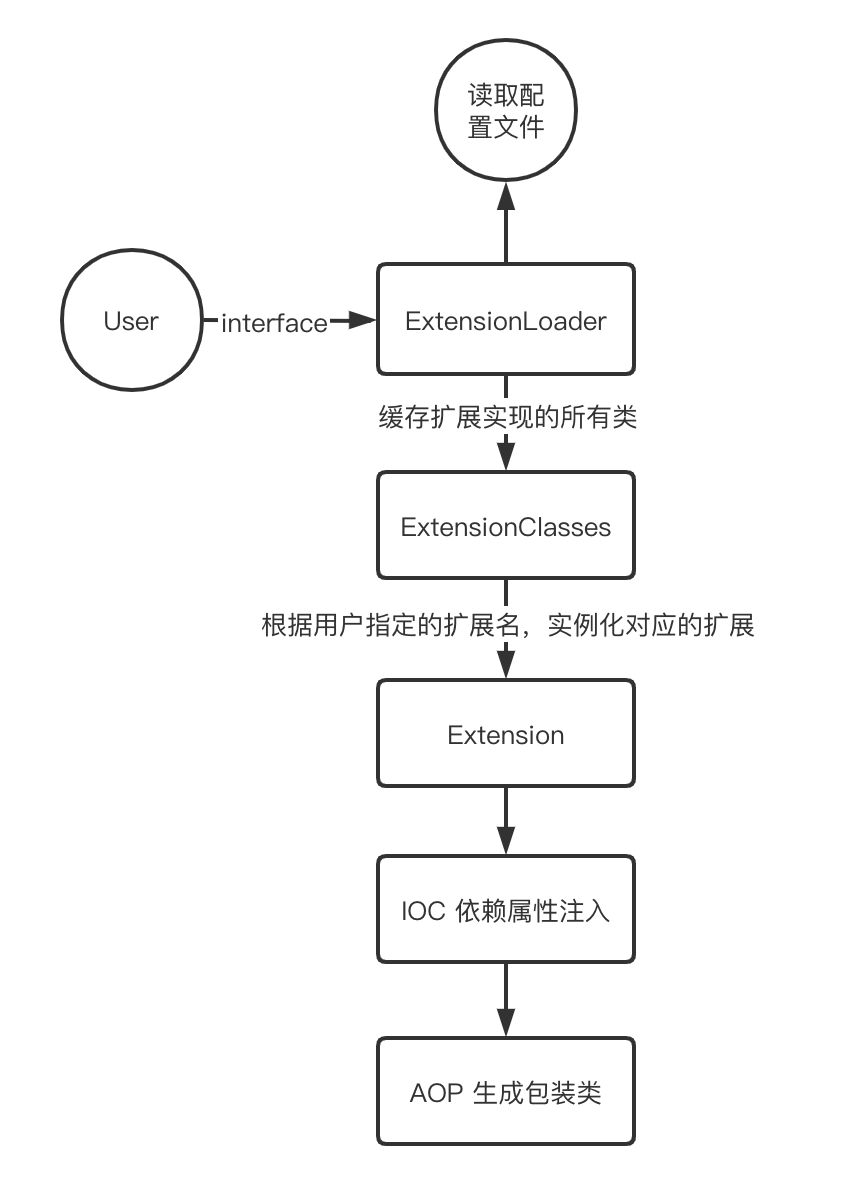
Dubbo SPI 补充一下Dubbo SPI 扩展能力的特性:
按需加载。Dubbo 的扩展能力不会一次性实例化所有实现,可以根据别名实例化指定的扩展类
增加扩展类的 IOC 能力。Dubbo 的扩展能力并不仅仅只是发现扩展服务实现类,而是在此基础上更进一步,如果该扩展类的属性依赖其他对象,则 Dubbo 会自动的完成该依赖对象的注入功能。
增加扩展类的 AOP 能力。Dubbo 扩展能力会自动的发现扩展类的包装类,完成包装类的构造,增强扩展类的功能。
具备动态选择扩展实现的能力。Dubbo 扩展会基于参数,在运行时动态选择对应的扩展类,提高了 Dubbo 的扩展能力。
可以对扩展实现进行排序。能够基于用户需求,指定扩展实现的执行顺序。
提供扩展点的 Adaptive 能力。该能力可以使的一些扩展类在 consumer 端生效,一些扩展类在 provider 端生效。
Dubbo SPI 加载扩展的工作流程:
参考: